1. hashtable
前置知识:【数据结构】3.跳表和散列
基本原理:
- 将Key计算成一个数值,然后取余数得到它在表头中的位置
- table(篮子)里每个指针都指向一个链表(桶)来存储余数相同的值
- 如果桶内的元素个数比篮子个数还多,则将篮子的大小扩充
- 篮子是vector,数量是质数,初始为53,53扩充后为97
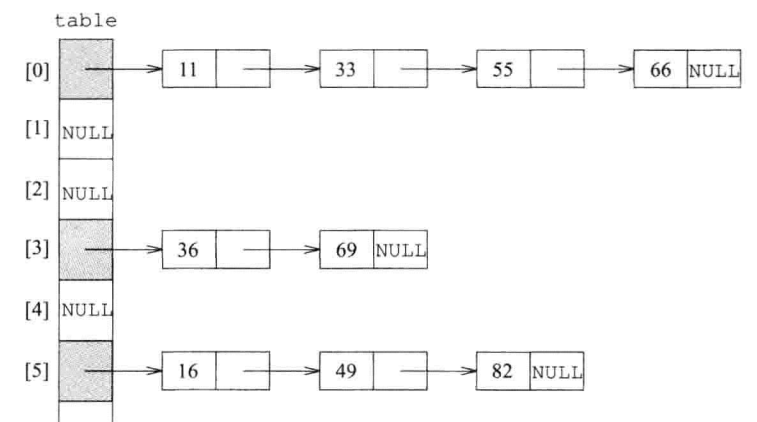
hashtable需要传入Value(Key+Data),Key,计算哈希的方法,从Value中取出Key的方法,比较Key是否相等的方法,以及分配器来实例化
1 | template <class Value, class Key, class HashFcn, class ExtractKey, class EqualKey, class Alloc=alloc> |
hashtable的篮子使用vector数组实现,迭代器中有两个指针,*cur指向当前元素位置,*ht指向它在篮子中的位置,实现操作者视角的++操作
1 | template <class Value, class Key, class HashFcn, class ExtractKey, class EqualKey, class Alloc> |
2. unordered_set / multi
第二个模板参数中,C++底层提供的哈希函数 hash
1 | template < class Key, //容器中存储元素的类型 |
3. unordered_map / multi
Key是键值对中的键、T是键值对中的data,<Key, T>组成hashtable中的Value。接下来的模板参数与unordered_set中相同
1 | template < class Key, //键值对中键的类型 |
4. unordered_map 和 map 对比
- map / set ,底层实现是红黑树
- + 自带排序的性质
- + 查找的时间复杂度是O(logn)
- - 每个节点都需要存储额外的信息
- unordered_map / unordered_set,底层是哈希表
- + 哈希表通过Key计算查找非常快 理想情况下是O(1)
- - 篮子数量>元素数量,每次扩充复制的时候比较耗时