1.问题引出
计算机中数据使用ascii码存储,而ascii码在128~255之间是不可见字符,网络上传输数据时往往经过多个路由设备,不同设备不同的处理方式也可能导致数据传输过程中处理出现问题。所以我们通过Base64将数据全部编码成可见字符(A-Z, a-z, 0-9, +, / 共64个)可以降低出错的可能。
- Base64应用:电子邮件的传输编码
- 附件中图片、音视频都是二进制的文件,但邮件传输协议只支持ASCII字符传递,所以普通的二进制文件传输无法实现
- HTTP协议要求请求行必须是ASCII编码
- 数据库读写 blob 中存储中文
- Base64算法
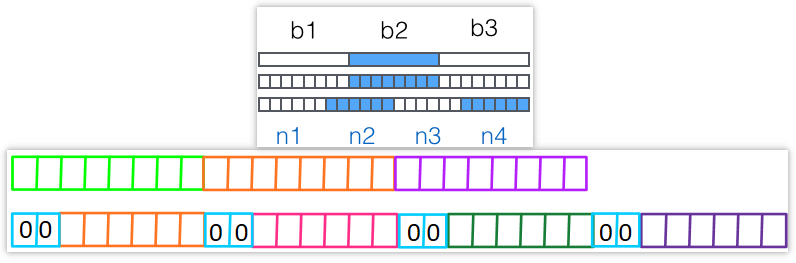
- 把一组3个字节转换成一组4个字节(编码后字符串变大了)
- 编码过程中如果最后一组3个字节凑不够,用0填充,输出字符使用’=’,可能补充1个或2个’=’来凑够3个字节一组
2. BIO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
BIO *BIO_new(const BIO_METHOD *type);
BIO_METHOD* BIO_f_base64();
BIO_METHOD* BIO_s_mem();
BIO *BIO_new_mem_buf(void *buf, int len);
BIO* BIO_new_file(const char* filename, const char* mode);
void BIO_free_all(BIO *a);
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
int BIO_read(BIO *b, void *buf, int len);
- buf: 存储数据的缓冲区地址
- len: buf的最大容量
int BIO_write(BIO *b, const void *buf, int len);
- buf: 要写入的数据, 写入到b对应的设备(内存/磁盘文件)中
- len: 要写入的数据的长度
int BIO_flush(BIO *b);
- 在使用BIO_write()进行写操作的时候, 数据有时候在openssl提供的缓存中
- 将openssl提供的缓存中的数据刷到设备(内存/磁盘文件)中
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
BIO * BIO_push(BIO *b, BIO *append);
- b: 要插入到链表中的头结点
- append: 头结点的后继
BIO * BIO_pop(BIO *b);
|
- 通过定义BUF_MEM* ptr; 并使用 BIO_get_mem_ptr 函数来获取数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| typedef struct buf_mem_st BUF_MEM;
struct buf_mem_st {
size_t length;
char *data;
size_t max;
unsigned long flags;
};
BUF_MEM* ptr;
long BIO_get_mem_ptr(BIO *b, BUF_MEM **pp);
|
- 一个BIO对象应用的例子,它可以很方便的完成一连串操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| BIO* md1 = BIO_new(xxx);
BIO* md2 = BIO_new(xxx);
BIO* b64 = BIO_new(xxx);
BIO* f = BIO_new(xxx);
BIO_push(b64, f);
BIO_push(md2, b64);
BIO_push(md1, md2);
int BIO_write(md1, "hello, world", 11);
|
2.1 Base64编解码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| char* data = "hello, world";
BIO* b64 = BIO_new(BIO_f_base64());
BIO* mem = BIO_new(BIO_s_mem());
BIO_push(b64, mem);
BIO_write(b64, data, strlen(data)+1);
BIO_flush(BIO *b);
BUF_MEM* ptr;
long BIO_get_mem_ptr(b64, &ptr);
char* buf = new char[ptr->length];
memcpy(buf, ptr->data, ptr->length);
printf("编码之后的数据: %s\n", buf);
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
char* data = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx";
BIO* b64 = BIO_new(BIO_f_base64());
BIO* mem = BIO_new(BIO_s_mem());
BIO_write(mem, data, strlen(data));
BIO_push(b64, mem);
char buf[1024];
int BIO_read(b64, buf, 1024);
printf("base64解码的数据: %s\n", buf);
|
Author:
mxwu
Permalink:
https://mingxuanwu.com/2023/12/09/202312091400/
License:
Copyright (c) 2023 CC-BY-NC-4.0 LICENSE