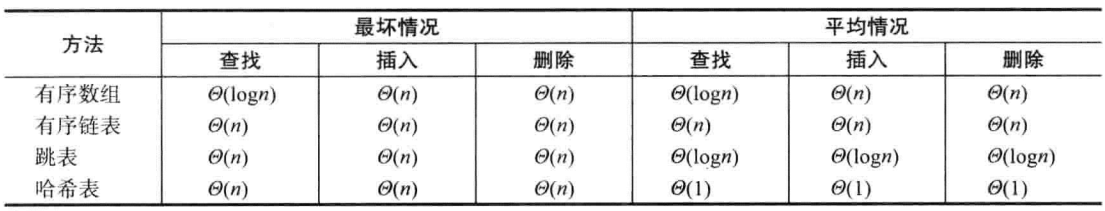
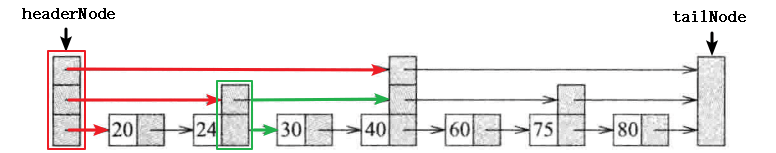
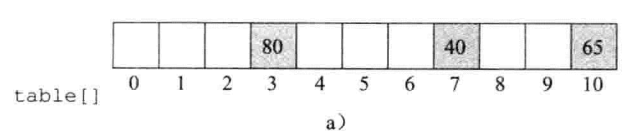
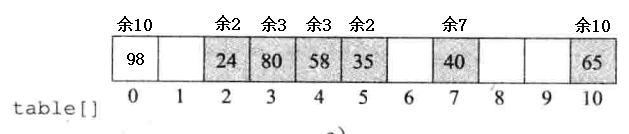
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
| #pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "dictionary.h"
#include "skipNode.h"
using namespace std;
template<class K, class E>
class skipList : public dictionary<K, E>
{
protected:
float cutOff;
int level() const;
int levels;
int dSize;
int maxLevel;
K tailKey;
skipNode<K, E>* search(const K&) const;
skipNode<K, E>* headerNode;
skipNode<K, E>* tailNode;
skipNode<K, E>** last;
public:
skipList(K, int maxPairs = 10000, float prob = 0.5);
~skipList();
bool empty() const { return dSize == 0; }
int size() const { return dSize; }
pair<const K, E>* find(const K&) const;
void erase(const K&);
void insert(const pair<const K, E>&);
void output() const;
};
template<class K, class E>
skipList<K, E>::skipList(K largeKey, int maxPairs, float prob)
{
cutOff = prob * RAND_MAX;
maxLevel = (int)ceil(logf((float)maxPairs) / logf(1 / prob)) - 1;
levels = 0;
dSize = 0;
tailKey = largeKey;
pair<K, E> tailPair;
tailPair.first = tailKey;
headerNode = new skipNode<K, E>(tailPair, maxLevel + 1);
tailNode = new skipNode<K, E>(tailPair, 0);
last = new skipNode<K, E> *[maxLevel + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= maxLevel; i++)
headerNode->next[i] = tailNode;
}
template<class K, class E>
skipList<K, E>::~skipList()
{
skipNode<K, E>* nextNode;
while (headerNode != tailNode)
{
nextNode = headerNode->next[0];
delete headerNode;
headerNode = nextNode;
}
delete tailNode;
delete[] last;
}
template<class K, class E>
pair<const K, E>* skipList<K, E>::find(const K& theKey) const
{
if (theKey >= tailKey)
return NULL;
skipNode<K, E>* beforeNode = headerNode;
for (int i = levels; i >= 0; i--)
while (beforeNode->next[i]->element.first < theKey)
beforeNode = beforeNode->next[i];
if (beforeNode->next[0]->element.first == theKey)
return &beforeNode->next[0]->element;
return NULL;
}
template<class K, class E>
int skipList<K, E>::level() const
{
int lev = 0;
while (rand() <= cutOff)
lev++;
cout << "它位于第" << lev << "级链表" << endl;
return (lev <= maxLevel) ? lev : maxLevel;
}
template<class K, class E>
skipNode<K, E>* skipList<K, E>::search(const K& theKey) const
{
skipNode<K, E>* beforeNode = headerNode;
for (int i = levels; i >= 0; i--)
{
while (beforeNode->next[i]->element.first < theKey)
beforeNode = beforeNode->next[i];
last[i] = beforeNode;
}
return beforeNode->next[0];
}
template<class K, class E>
void skipList<K, E>::insert(const pair<const K, E>& thePair)
{
if (thePair.first >= tailKey)
{
cout << "关键字过大" << endl;
return;
}
skipNode<K, E>* theNode = search(thePair.first);
if (theNode->element.first == thePair.first)
{
theNode->element.second = thePair.second;
return;
}
int theLevel = level();
if (theLevel > levels)
{
theLevel = ++levels;
last[theLevel] = headerNode;
}
skipNode<K, E>* newNode = new skipNode<K, E>(thePair, theLevel + 1);
for (int i = 0; i <= theLevel; i++)
{
newNode->next[i] = last[i]->next[i];
last[i]->next[i] = newNode;
}
dSize++;
return;
}
template<class K, class E>
void skipList<K, E>::erase(const K& theKey)
{
if (theKey >= tailKey)
return;
skipNode<K, E>* theNode = search(theKey);
if (theNode->element.first != theKey)
return;
for (int i = 0; i <= levels && last[i]->next[i] == theNode; i++)
last[i]->next[i] = theNode->next[i];
while (levels > 0 && headerNode->next[levels] == tailNode)
levels--;
delete theNode;
dSize--;
}
template<class K, class E>
void skipList<K, E>::output() const
{
skipNode<K, E>* p;
for (int i = levels; i >= 0; i--)
{
p = headerNode;
while (p->next[i]->element.first < tailKey)
{
p = p->next[i];
cout << p->element.second << ", ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
|